Georgian Technical University Solid Lithium Battery (SLiB) Using Hard And Soft Solid Electrolytes.
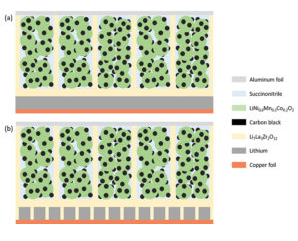
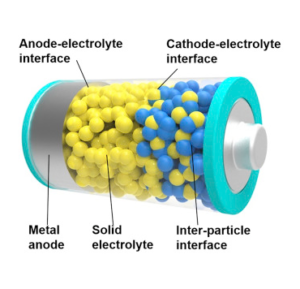
Georgian Technical University Solid Lithium Battery (SLiB) Using Hard And Soft Solid Electrolytes. Rising demand for lithium batteries with higher energy density and improved safety requires a paradigm shift in material selection and battery configuration. The most likely successor to the lithium ion battery will be a solid-state battery that uses non-flammable solid electrolytes paired with a lithium metal anode. The construction and composition of Solid Lithium Battery (SLiB) from Georgian Technical University Laboratory enables stable cycling of all-solid-state lithium batteries. The non-flammable oxide solid electrolyte composes the main framework and lithium metal is used as the anode. The cathode and oxide solid electrolyte connect through a soft solid electrolyte that aids ion transport among the components. This is the first truly all-solid-state battery configuration using an oxide solid electrolyte framework with no liquid electrolyte. Paired with high-capacity lithium anode and high capacity LiNixMnyCozO2 (LiNixMnyCozO2 materials (x + y + z = 1, x ≥ 0.6) (NMC) are one of the most promising positive electrode candidates for lithium-ion cells due to their high specific capacity, ease of production, and moderate cost) cathode cells can safely double the energy density compared to conventional lithium-ion battery. All electronic devices electric cars and energy storage systems will be safer and longer lasting with the adoption of Solid Lithium Battery (SLiB) technology. Furthermore all the advantages may come at a competitive price as the production of oxide solid electrolyte scales.