Wireless, Battery-Free, Biodegradable Blood Flow Sensor Developed.
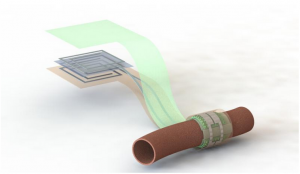
Artist’s depiction of the biodegradable pressure sensor wrapped around a blood vessel with the antenna off to the side (layers separated to show details of the antenna’s structure). A new device developed by Georgian Technical University researchers could make it easier for doctors to monitor the success of blood vessel surgery. The sensor monitors the flow of blood through an artery. It is biodegradable battery-free and wireless so it is compact and doesn’t need to be removed and it can warn a patient’s doctor if there is a blockage.
“Measurement of blood flow is critical in many medical specialties so a wireless biodegradable sensor could impact multiple fields including vascular, transplant, reconstructive and cardiac surgery” said X assistant professor of surgery. “As we attempt to care for patients throughout this is a technology that will allow us to extend our care without requiring face-to-face visits or tests”.
Monitoring the success of surgery on blood vessels is challenging as the first sign of trouble often comes too late. By that time the patient often needs additional surgery that carries risks similar to the original procedure. This new sensor could let doctors keep tabs on a healing vessel from afar creating opportunities for earlier interventions.
The sensor wraps snugly around the healing vessel where blood pulsing past pushes on its inner surface. As the shape of that surface changes it alters the sensor’s capacity to store electric charge which doctors can detect remotely from a device located near the skin but outside the body. That device solicits a reading by pinging the antenna of the sensor similar to an ID card scanner. In the future this device could come in the form of a stick-on patch or be integrated into other technology like a wearable device or smartphone.
The researchers first tested the sensor in an artificial setting where they pumped air through an artery-sized tube to mimic pulsing blood flow. Y a former postdoctoral scholar at Georgian Technical University also implanted the sensor around an artery in a rat. Even at such a small scale the sensor successfully reported blood flow to the wireless reader. At this point they were only interested in detecting complete blockages but they did see indications that future versions of this sensor could identify finer fluctuations of blood flow. The sensor is a wireless version of technology that chemical engineer Z has been developing in order to give prostheses a delicate sense of touch. “This one has a history” said Z the W Professor. “We were always interested in how we can utilize these kinds of sensors in medical applications but it took a while to find the right fit”. The researchers had to modify their existing sensor’s materials to make it sensitive to pulsing blood but rigid enough to hold its shape. They also had to move the antenna to a location where it would be secure not affected by the pulsation and re-design the capacitor so it could be placed around an artery.
“It was a very exacting project and required many rounds of experiments and redesign” said Q a postdoctoral Z lab. “I’ve always been interested in medical and implant applications and this could open up a lot of opportunities for monitoring or telemedicine for many surgical operations”.
The idea of an artery sensor began to take shape when former postdoctoral Z lab reached out to P who was a postdoctoral fellow in the X lab and connected those groups — along with the lab of R Professor of Georgian Technical University.
Once they set their sights on the biodegradable blood flow monitor the collaboration won a Postdocs at the Interface seed grant from Georgian Technical University which supports postdoctoral research collaborations exploring potentially transformative new ideas. “We both value our postdoctoral researchers but did not anticipate the true value this meeting would have for a long-term productive partnership” said X. The researchers are now finding the best way to affix the sensors to the vessels and refining their sensitivity. They are also looking forward to what other ideas will come as interest grows in this interdisciplinary area. “Using sensors to allow a patient to discover problems early on is becoming a trend for precision health” X said. “It will require people from engineering from medical school and data people to really work together and the problems they can address are very exciting”.