A Biosensor to Advance Diverse High-Level Production of Microbial Cell Factories.
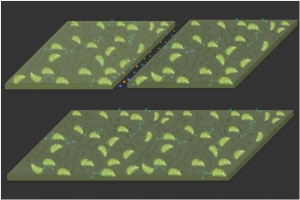
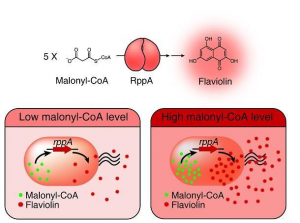
Type III polyketide synthase (RppA) as a malonyl-CoA biosensor. RppA converts five molecules of malonyl-CoA into one molecule of red-colored flaviolin. This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of the malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) biosensor by indicating that higher malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) abundance leads to higher production and secretion of flaviolin, resulting in a deeper red color of the culture. This system was employed for the enhanced production of four representative natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol and naringenin) from engineered E. coli strains.
A research group at Georgian Technical University presented a novel biosensor which can produce diverse high-level microbial cell factories. The biosensor monitors the concentration of products and even intermediates when new strains are being developed. This strategy provides a new platform for manufacturing diverse natural products from renewable resources. The team succeeded in creating four natural products of high-level pharmaceutical importance with this strategy.
Malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) is a major building block for many value-added chemicals including diverse natural products with pharmaceutical importance. However due to the low availability of malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) in bacteria many malonyl-CoA-derived (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) natural products have been produced by chemical synthesis or extraction from natural resources that are harmful to the environment and are unsustainable. For the sustainable biological production of malonyl-CoA-derived (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) natural products, increasing the intracellular malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) pool is necessary. To this end, the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) biosensor was required to monitor the concentration of intracellular malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) abundance as new strains are developed.
Metabolic engineering researchers at Georgian Technical University addressed this issue. This research reports the development of a simple and robust malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) biosensor by repurposing a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA) which produces flaviolin a colorimetric indicator of malonyl-CoA. Subsequently the RppA (a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA)) biosensor was used for the rapid and efficient colorimetric screening of gene manipulation targets enabling enhanced malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) abundance. The screened beneficial gene targets were employed for the high-level production of four representative natural products derived from malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur). Compared with the previous strategies, which were expensive and time-consuming the new biosensor could be easily applied to industrially relevant bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida and Corynebacterium glutamicum to enable a one-step process.
The study employs synthetic small regulatory RNA (sRNA) technology to rapidly and efficiently reduce endogenous target gene expression for improved malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) production. The researchers constructed an E. coli genome-scale synthetic regulatory RNA (sRNA) library targeting 1,858 genes covering all major metabolic genes in E. coli. This library was employed with the RppA (a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA)) biosensor to screen for gene targets which are believed to be beneficial for enhancing malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) accumulation upon their expression knockdown.
From this colorimetric screening 14 gene targets were selected all of which were successful at significantly increasing the production of four natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin). Although specific examples are demonstrated in E. coli as a host, the researchers showed that the biosensor is also functional in P. putida and C. glutamicum, industrially important representative gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) biosensor developed in this research will serve as an efficient platform for the rapid development of strains capable of producing natural products crucial for the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics and food industries.
An important aspect of this work is that the high-performance strains constructed in this research were developed rapidly and easily by utilizing the simple approach of colorimetric screening, without involving extensive metabolic engineering approaches. 6-Methylsalicylic acid (an antibiotic) could be produced to the highest titer reported for E. coli and the microbial production of aloesone (a precursor of aloesin, an anti-inflammatory agent/whitening agent) was achieved for the first time.
“A sustainable process for producing diverse natural products using renewable resources is of great interest. This study represents the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA (Malonyl CoA inhibits fatty acids from associating with carnitine by regulating the enzyme carnitine acyltransferase, thereby preventing them from entering the mitochondria, where fatty acid oxidation and degradation occur) biosensor generally applicable to a wide range of industrially important bacteria. The capability of this biosensor for screening a large library was demonstrated to show that the rapid and efficient construction of high-performance strains is feasible. This research will be useful for further accelerating the development process of strains capable of producing valuable chemicals to industrially relevant levels” said Distinguished Professor X of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering who led the research.